Space-based services for society
Updated December 2025
Read more
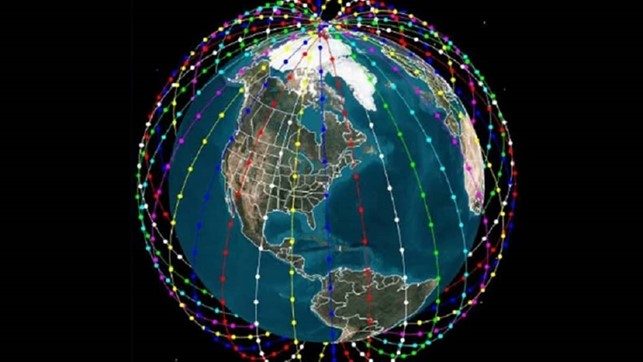
Space applications have a particular impact on the following areas: positioning, navigation, precise time, communications, meteorological observations, remote mapping and imaging as well as science & research. Space-based location, navigation and time services (Positioning, Navigation and Timing, PNT) such as GPS, Glonass, BeiDou and Galileo enable the satellite to be used for navigation and many routine functions. They support sea, land, and air transport, for example in route planning and congestion management. For the military, this information makes it possible to accurately target missiles and ammunition, as well as navigate aircraft, troops and ships.
Of the PNT signals, accurate time service also supports critical infrastructure. Without accurate time, financial institutions would not be able to create timestamps for transactions, which would affect the use of ATMs and credit cards. Nor would electricity companies be able to transmit electricity efficiently.
The loss of communications satellites could have wide-ranging effects. In 1998, an American telecommunications satellite suffered a computer failure. As a result, people couldn’t pay for fuel, hospitals couldn’t get in touch with doctors who relied on pagers, and television stations couldn’t broadcast programs. In the armed forces, satellite communications improve situational awareness and increase troop mobility.
Weather observation and remote mapping satellites provide terrain and environmental data that help businesses determine the viability of mineral resources and help farmers identify potential agricultural disasters. These satellites also support military activities by providing intelligence and surveillance data.
Society has greatly benefited from technologies made possible by space exploration. These include phone cameras, solar panels, laptops, and compact water purification systems.
The development of mini- and microsatellite technology has greatly expanded the commercial use of space. One such Nordic company is the Finnish ICEYE, founded in 2014. It is developing a service that utilises microsatellites equipped with SAR radars to provide near-real-time radar imagery, regardless of time or weather conditions. The Swedish company, Ovzon, provides broadband and mobile communications via satellite. Its Ovzon-3 satellite was launched aboard SpaceX’s Falcon 9 in January 2024.
In 2019, the SpaceX and OneWeb companies began deploying low-orbit (LEO) satellites to provide high-speed internet access worldwide. The number of low-orbit satellites had almost doubled by the end of 2020. SpaceX has already launched more than 5,000 Starlink satellites into space and plans to launch up to 12,000 of them within the next few years. The mission of the Starlink system is to provide high-speed internet access anywhere on Earth. Up to 60 Starlink satellites will be launched at the same time. Starlink satellites are relatively small telecommunications satellites whose task is to create a high-speed data network that reaches half of our planet.
Several other companies are also building similar networks around the globe. In the future, it will be possible to connect to the Internet via a mega constellation from anywhere, anytime, cheaply and simply.
OneWeb, owned by Eutelsat, has rapidly expanded its coverage, and its satellites cover the whole of Europe. About 580 OneWeb satellites are currently in orbit. Amazon has launched the first 27 Kuiper internet satellites, with 1,618 planned by June 2026 and a final constellation of 3,236 satellites.
SpaceX manufactures and operates space rockets and spacecraft as well as develops the Starlink satellite internet system. The company’s products include the partially reusable Falcon 9 and Falcon Heavy launchers, as well as the Dragon spacecraft, whose second version is crewed and the fully reusable Starship spacecraft and its Superheavy launcher. As of February 2025, Falcon 9 has completed 435 launches.
Sources and links
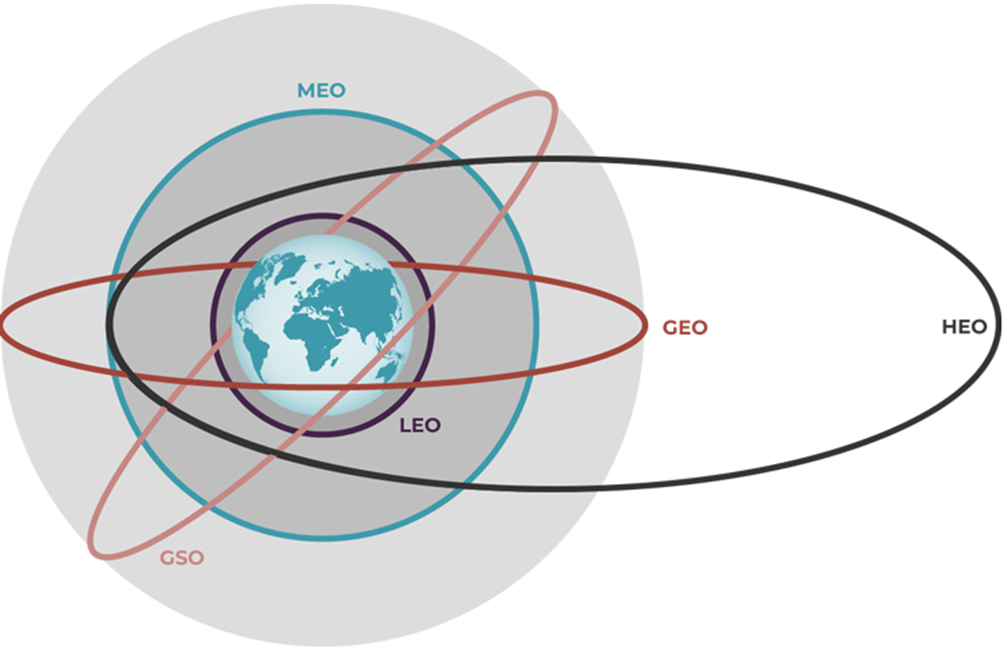
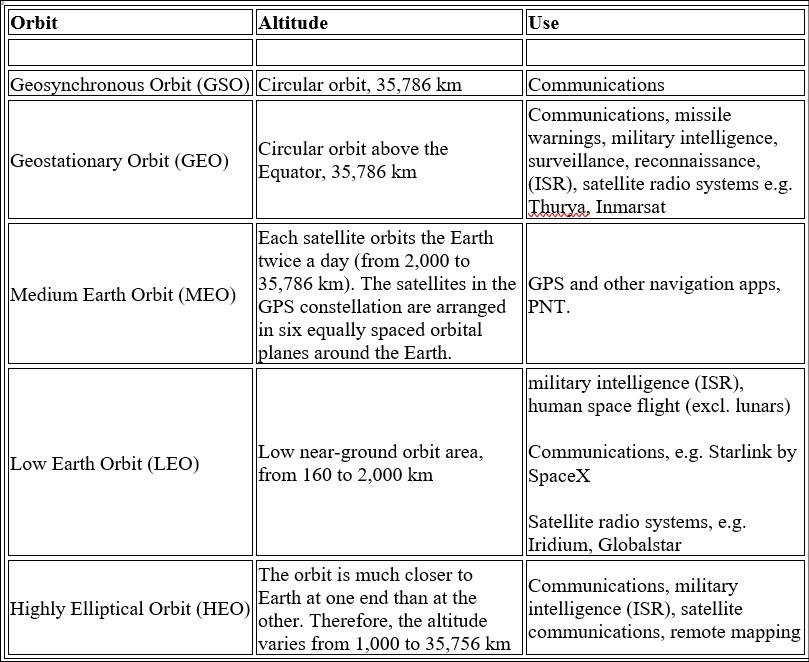
Types of orbits:
https://www.esa.int/Enabling_Support/Space_Transportation/Types_of_orbits
What is Positioning, Navigation and Timing (PNT)? US Dept. of Transportation 2025:
https://www.transportation.gov/pnt/what-positioning-navigation-and-timing-pnt