Israel, Palestinian territories, Lebanon, Yemen, Iran
Current topics, April 2025.
The terrorist organization Hamas’ surprise attack from Gaza on Israel in October 2023 started a new spiral of violence in the Middle East. Israel retaliated by launching massive attacks on Gaza to destroy Hamas and their operating capabilities in Gaza. The military operations expanded into Lebanese territory when the Iranian-backed terrorist organization Hezbollah launched rocket attacks on Northern Israel. The fall of President Assad’s regime in Syria on 8 December 2024 further amplified regional imbalance.
In a surprise attack on Israel on October 7, 2023, Hamas killed more than 1,100 Israeli civilians and took 250 hostages from Israel to Gaza. Israel responded with vigorous military action aimed at the complete destruction of Hamas. Over the years, Hamas has built up an extensive underground support network of tunnels and uses above-ground infrastructure for its operations. Attacks by the Israeli armed forces have devastated large areas of Gaza, and tens of thousands of people have died. In January 2025, Israel and Hamas signed a three-phase truce agreement that was intended to lead to a permanent ceasefire and the release of Israeli hostages. However, both sides have violated the agreement, and a possible ceasefire is now uncertain.
An initiative of the new US administration has brought on an additional element to the situation in the Middle East. It includes, among other things, a proposal to evacuate the population of Gaza and rebuild it under the leadership of the United States.
Israeli attacks in the West Bank have increased. Israel has launched targeted air strikes on the area and ordered the population to relocate.
In Southern Lebanon, Hezbollah has fired hundreds of rockets and drones at Israel. As a response, Israel has initiated aerial bombardments and ground attacks. Israel has also succeeded in destroying Hezbollah’s top leadership. In November 2024, Israel and Hezbollah signed a ceasefire agreement, but the ceasefire has been violated. Despite the agreement, Israel intends to permanently operate five military bases in Southern Lebanon.
The Houthi terrorist group, which has been rebelling against the Yemeni government, began attacks on Israel and Western merchant vessels in the Red Sea, demanding that Israel stop its attack on Gaza. They have attacked dozens of Western merchant vessels and warships with missiles, rockets, and drones, as well as military bases of the United States and its allies. Due to the Houthi attacks, hundreds of merchant vessels have been diverted to a longer route around the coast of Africa.
In 2023, the US-led international operation Prosperity Guardian, in which more than 20 countries participated, was launched to secure shipping in the Red Sea and the Gulf of Aden. Finland has sent two officers to the headquarters of the operation. The UN Security Council has condemned the Houthi attacks (Resolution 2722, January 2024).
Iran and Israel have been plunged into a near-open conflict after Israel carried out an airstrike on the Iranian consulate in Damascus in April 2024. Leaders of the Iranian Revolutionary Guard Corps were killed in the attack. Since then, Israel has killed key leaders of Iranian-backed Hamas and Hezbollah. A special feature of the attack was carried out with the help of tracking devices, which targeted nearly 3,000 members of Hezbollah. Israel and Iran have repeatedly launched missile strikes on each other’s targets, and this is believed to increase the risk of escalation of the crisis.
The Axis of Resistance is an unofficial coalition of Iranian-backed militants and political organizations in Lebanon, Iraq, Syria, Yemen, and Gaza, among others. The Axis’s goal is to make Israel’s attacks more difficult and to incur costs on the United States for its support of Israel. The coalition has also carried out attacks against US troops in Iraq. Iran has provided extensive military and logistical support to the Axis, although recent military actions by Israel and the United States have weakened the coalition.
The détente development in the Middle East before 2023 included Israel’s diplomatic relations with Jordan, Egypt, Sudan, Bahrain, Morocco, and the United Arab Emirates, based on the 2020 Abraham Accords agreement. It seemed that Saudi Arabia would also join the agreement, but Hamas’ October 7 attack and Israel’s retaliatory measures in Gaza have halted this development.
In Iran, détente may have been seen as a shift in the regional balance of power in favour of Israel and Saudi Arabia. Iran has increased its support for rebel movements operating in the region, regardless of their religious affiliation (Hamas and the Muslim Brotherhood of Egypt being Sunnis, and Hezbollah and Houthi Shiites).
The strategic balance in the Middle East is changing. The reason for this is the setbacks experienced by Iran and its proxies, Hezbollah and Hamas, as well as the fall of the Assad regime in Syria. Israel has seized the UN buffer zone in the Golan Heights and is occupying the area. According to Prime Minister Netanyahu, Israel will not allow Syrian government troops to be deployed South of Damascus and demands the demilitarization of several Syrian provinces.
Sources: CNN, Wall Street Journal, Al-Jazeera, CBS News, Al-Monitor, The New Arab, The New York Times, Reuters, Bloomberg, BBC News, Sky News, AP, AFP, Institute for Study of War (ISW), Critical Threats (CT), International Crisis Group – CrisisWatch (ICG), Encyclopædia Britannica
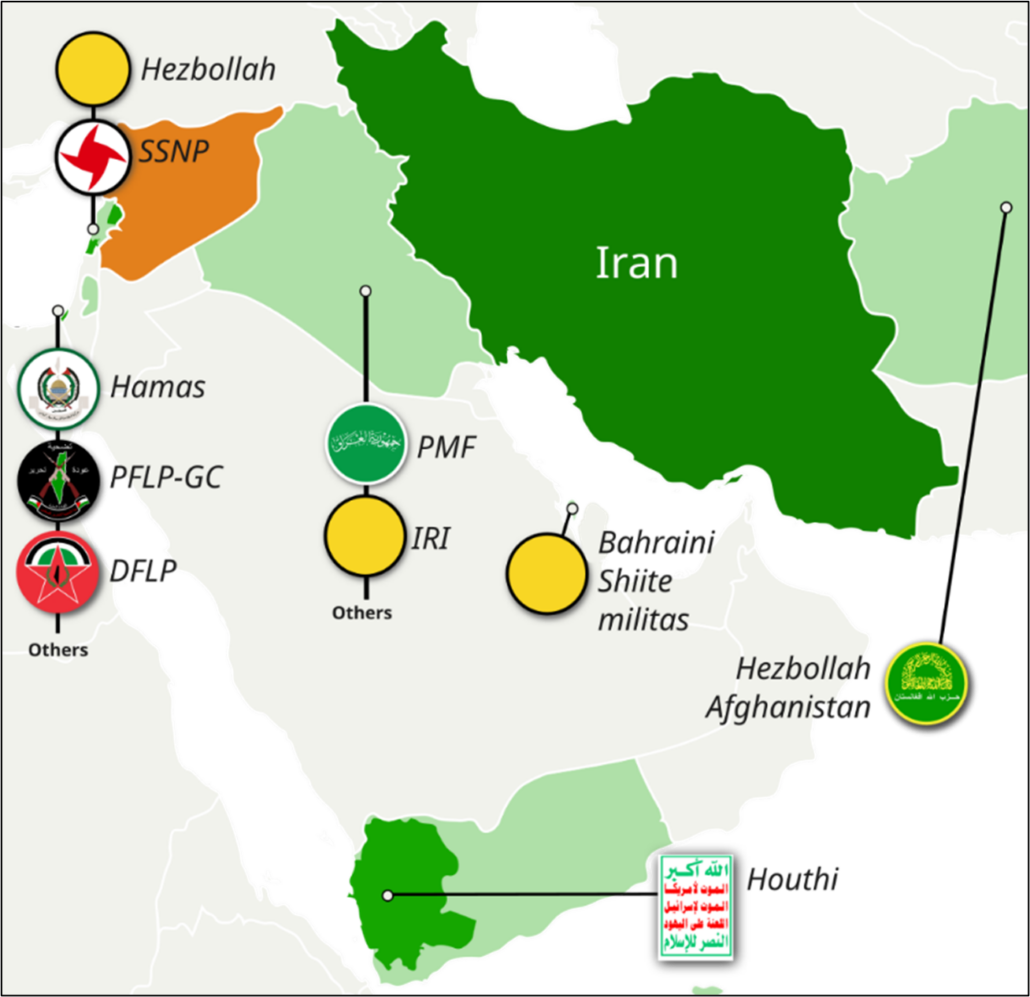
”The Axis of Resistance”. Source: Wikimedia Commons, https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Axis_of_Resistance.svg

Israeli operations in Lebanon, February 2025. Source: Institute for the Study of War (ISW) and Critical Threats (CT),, https://www.understandingwar.org/backgrounder/iran-update-february-17-2025.
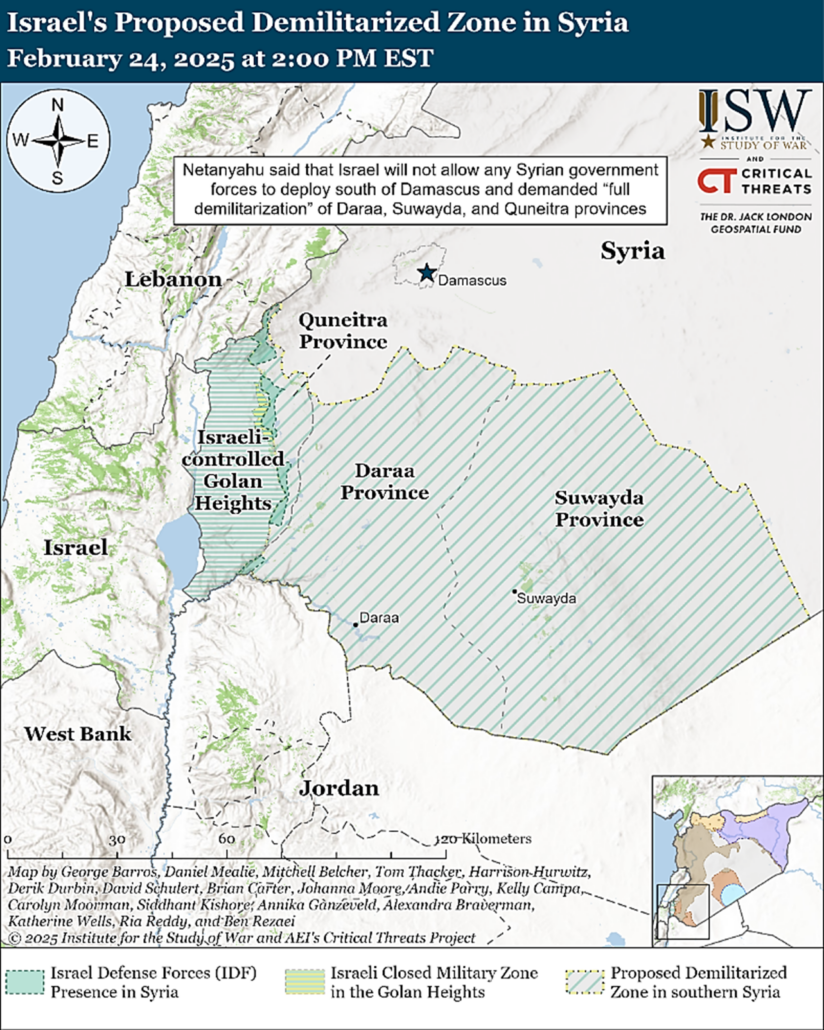
Israel’s demand for a demilitarized zone in Syria. Source: Institute for the Study of War (ISW) and Critical Threats (CT), https://www.understandingwar.org/backgrounder/iran-update-february-24-2025.

